The Jacobian Matrix
Consider a function that maps reals to reals,
This is pretty simple to do, and follows from taylor’s expansion upto the first order.
Let’s try expanding this concept to vector spaces. For a function
(bold type indicates vectors). This also follows from the taylor theorem for multivariable functions.
What do we do when we have a function mapping vector spaces to vector spaces?
Consider the function
Let’s try to solve this by decomposing the function
If we collect all these approximations into a vector by representing the term
I’ve written the functions out in matrix form for clarity.
Here,
The Jacobian Matrix thus, is an analog of the gradient vector for functions that
map vector spaces to vector spaces. Everything that we can do using gradients
can be done in a more general form using the Jacobian Matrix. Consider the
condition for differentiability of a multivariate scalar function
For a function
here,
Relating Jacobian Matrices and Transformation Matrices
If you notice, the Jacobian Matrix need not be square; for the special case
Therefore, this acts like a linear transformation between the infinitesimal
elements in the space of
Scaling factor and the Jacobian Determinant
Recall that for any linear transformation, the determinant of the transformation gives us the scaling factor, that is the ratio of the change in ‘volume’ occupied by the vector. This is also known as a dilation transformation (because just the size is involved, without worrying about orientation).
I’ll provide a proof for the statement highlighted above in
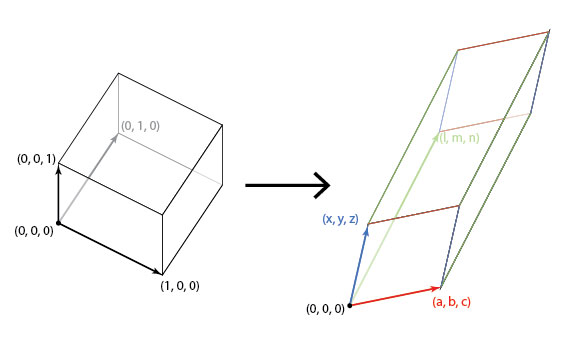
In algebra terms, we get
The volume of a parallelepiped is given by the determinants of the 3 edge vectors, and hence the volume of the transformed cube is
Which is the determinant of the linear transform that we started with.
This is the main principle that allows us to use the Jacobian in multiple integrals while changing variables: it scales up or down the size of the area or volume element we are using proportionately to the change of variables.
References:
- What is the Jacobian Matrix, a good MSE thread on the Jacobian Matrix
- Jacobian Matrix and Determinant Wikipedia page, of course
- A Quora question on Jacobian matrices with another very nice answer